基本の角度のついた跳ね返り
水平面や垂直面に対する跳ね返りは、単に速度を反転させればよく簡単だが(【JavaScript】ボールを壁で跳ね返させる)、反射面に角度がついている場合は難しい。そこで、ボールが反射面に当たった時、システムの座標を変換して反射面を水平にし、跳ね返り処理を行った後、システムの座標を元に戻す方法を採用する。
下のスクリプトはCanvasに反射面である線を引き、上から落としたボールを跳ね返らせている。
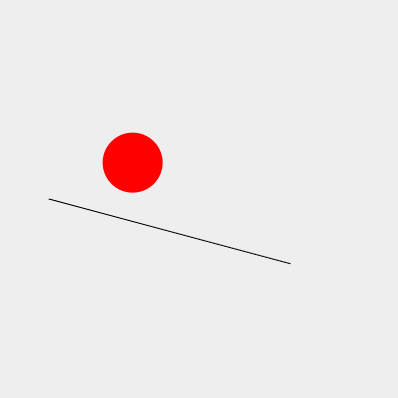
まず、ボールに見立てた円を描画するCircleクラス。
/**
* 真円を描画(circle.js)
*/
export class Circle {
constructor(parent = undefined, x = 0, y = 0, radius = 15) {
if (parent !== undefined) {
this._parent = parent;
}
this._x = x;
this._y = y;
this._radius = radius;
this._color = "#ff0000";
this._init();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Private and protected
//////////////////////////////////
_init() {
if (this._parent !== undefined) {
this._ctx = this._parent;
}
this.draw();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Public
//////////////////////////////////
draw() {
this._ctx.save();
this._ctx.fillStyle = this._color;
this._ctx.beginPath();
this._ctx.arc(this._x, this._y, this._radius, 0, (Math.PI * 2), true);
this._ctx.closePath();
this._ctx.fill();
this._ctx.restore();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Getters/Setters
//////////////////////////////////
get x() {
return this._x;
}
set x(x) {
this._x = x;
}
get y() {
return this._y;
}
set y(y) {
this._y = y;
}
get radius() {
return this._radius;
}
set radius(radius) {
this._radius = radius;
}
set color(color) {
this._color = color;
this.draw();
}
}
次に、線を描画するLineクラス。
/**
* 反射面を描画(line.js)
* @param parent 親のコンテキスト
* @param x1 描き始めのX座標
* @param y1 描き始めのY座標
* @param x2 描き終わりのX座標
* @param y2 描き終わりのY座標
*/
export class Line {
constructor(parent = undefined, x1 = 0, y1 = 0, x2 = 0, y2 = 0) {
if (parent !== undefined) {
this._parent = parent;
}
this._x = 0;
this._y = 0;
this._x1 = x1;
this._y1 = y1;
this._x2 = x2;
this._y2 = y2;
this._rotation = 0;
this._lineWidth = 1;
this._init();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Private and protected
//////////////////////////////////
_init() {
if (this._parent !== undefined) {
this._ctx = this._parent;
}
this.draw();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Public
//////////////////////////////////
draw() {
this._ctx.save();
this._ctx.translate(this._x, this._y);
this._ctx.rotate(this._rotation);
this._ctx.lineWidth = this._lineWidth;
this._ctx.beginPath();
this._ctx.moveTo(this._x1, this._y1);
this._ctx.lineTo(this._x2, this._y2);
this._ctx.closePath();
this._ctx.stroke();
this._ctx.restore();
}
/**
* 線の描画領域(矩形)を返す
* @returns オブジェクトでx、y、幅、高さ
*/
getBounds() {
// 線の角度が0度(水平)なら実行
if (this._rotation === 0) {
let minX = Math.min(this._x1, this._x2);
let minY = Math.min(this._y1, this._y2);
let maxX = Math.max(this._x1, this._x2);
let maxY = Math.max(this._y1, this._y2);
return {
x: this._x + minX,
y: this._y + minY,
width: maxX - minX,
height: maxY - minY
}
// 線の角度が0以外なら実行
} else {
let sin = Math.sin(this._rotation);
let cos = Math.cos(this._rotation);
let x1r = cos * this._x1 + sin * this._y1;
let x2r = cos * this._x2 + sin * this._y2;
let y1r = cos * this._y1 + sin * this._x1;
let y2r = cos * this._y2 + sin * this._x2;
return {
x: this._x + Math.min(x1r, x2r),
y: this._y + Math.min(y1r, y2r),
width: Math.max(x1r, x2r) - Math.min(x1r, x2r),
height: Math.max(y1r, y2r) - Math.min(y1r, y2r)
}
}
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Getters/Setters
//////////////////////////////////
get x() {
return this._x;
}
set x(x) {
this._x = x;
}
get y() {
return this._y;
}
set y(y) {
this._y = y;
}
get rotation() {
return this._rotation;
}
set rotation(rotation) {
this._rotation = rotation;
}
}
最後に、角度のついた跳ね返りを処理するAngleBounceクラス。
import { Line } from "./line.js";
import { Circle } from "./circle.js";
/**
* 角度のついた跳ね返り運動(anglebounce.js)
*/
export class AngleBounce {
constructor() {
this._cvs = document.getElementById('canvas');
this._ctx = this._cvs.getContext('2d');
this._line;
this._circle;
this._gravity = 0.2;
this._bounce = -0.6;
this._vx = 0;
this._vy = 0;
// タイマー関連
this._animID;
this._isAnim = 0;
this._FPS = 60;
this._frame = 0;
this._startTime;
this._nowTime;
this._init();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Private and protected
//////////////////////////////////
_init() {
this._cvs.style.backgroundColor = "#eeeeee";
// ①角度のついた反射面を描画
this._line = new Line(this._ctx, 0, 0, 250, 0);
this._line.x = 50;
this._line.y = 200;
// ②角度をラジアンに変換して渡す
this._line.rotation = 15 * Math.PI / 180;
this._circle = new Circle(this._ctx, 100, 100, 30);
this._startTime = performance.now();
this._mainLoop();
}
_mainLoop() {
this._nowTime = performance.now();
let elapsedTime = this._nowTime - this._startTime;
let idealTime = this._frame * (1000 / this._FPS);
if (idealTime < elapsedTime) {
this._ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this._cvs.width, this._cvs.height);
// ③ボールに速度を設定.Y軸に重力値を適用
this._vy += this._gravity;
this._circle.x += this._vx;
this._circle.y += this._vy;
// ④角度のサインとコサインを取得
let cos = Math.cos(this._line.rotation);
let sin = Math.sin(this._line.rotation);
// ⑤斜線を基準にしたボールの位置の取得
let x1 = this._circle.x - this._line.x;
let y1 = this._circle.y - this._line.y;
// ⑥座標の回転
let x2 = cos * x1 + sin * y1;
let y2 = cos * y1 - sin * x1;
// ⑦速度の回転
let vx1 = cos * this._vx + sin * this._vy;
let vy1 = cos * this._vy - sin * this._vx;
// ⑧ボールが斜線に当たったか判定
if (y2 > 0 - this._circle.radius) {
// ⑨回転させた値を使った跳ね返りの実行
y2 = -this._circle.radius;
vy1 *= this._bounce;
}
// ⑩全てを回転させて元状態に戻す
x1 = cos * x2 - sin * y2;
y1 = cos * y2 + sin * x2;
this._vx = cos * vx1 - sin * vy1;
this._vy = cos * vy1 + sin * vx1;
this._circle.x = this._line.x + x1;
this._circle.y = this._line.y + y1;
this._circle.draw();
this._line.draw();
this._frame++;
if (elapsedTime >= 1000) {
this._startTime = this._nowTime;
this._frame = 0;
}
}
this._animID = requestAnimationFrame(this._mainLoop.bind(this));
}
}
requestAnimationFrameを使ったゲームループの実装は、「【JavaScript】requestAnimationFrameでゲームループを作る」を参照。
①まず反射面である線をX座標50、Y座標200の地点に描画。②角度は15度でラジアンに変換している。
③最初に重力値をボールのY軸に加算。さらに速度をボールに適用。
④線の角度を使いサインとコサインを取得。後に回転する時に使用。
⑤線の位置を基準にしたボールのX、Y座標を、ボールの位置から線の位置を引くことで求める。これが回転の中心点となる。
⑥座標の回転。回転のやり方は「【JavaScript】オブジェクトを円運動させる【JavaScript】オブジェクトを円運動させる」の後半で解説している。③で線の角度を元にサインとコサインを出しているため、同じ角度量回転して水平になる。
⑦速度も同じように回転させる。速度は角度と大きさ(長さ)を持つベクトルのため、角度が分かれば回転可能。
⑧ボールが跳ねる下の境界は0となる線自体のため、y2が0からボールの半径を引いた値よりも大きいかどうかで、当たり判定を行っている。
⑨線に上に来るようボール位置を調整し、跳ね返りの値を適用して跳ね返させる。
⑩全てを回転させて元状態に戻す。逆回転させるため下4行の+と-を逆にしている。元の座標を変数で保存しておくよりも手軽。
線から落ちるようにする
このままでは、線上を通り過ぎても転がり続けるため、ボールが線上にあるか判定を行う。判定処理を追加したのがAngleBounce2クラス。
AngleBounceクラスの③箇所の上に、
let bounds = this._line.getBounds();を追加。線の描画領域を矩形情報(X座標、Y座標、幅、高さ)を取得。
さらに、④〜⑩までを以下のif文で囲っただけ。
if (this._circle.x + this._circle.radius > bounds.x
&& this._circle.x - this._circle.radius < bounds.x + bounds.width) {
...
}スクリプトとコードは以下。
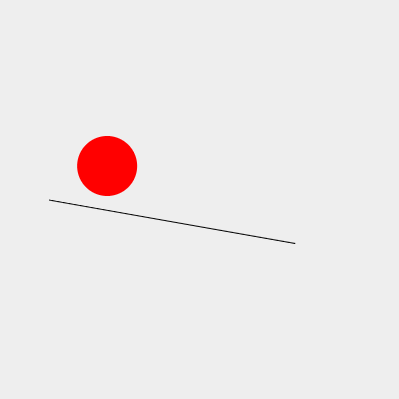
import { Line } from "./line.js";
import { Circle } from "./circle.js";
/**
* 角度のついた跳ね返り運動2(anglebounce2.js)
*/
export class AngleBounce2 {
constructor() {
this._cvs = document.getElementById('canvas');
this._ctx = this._cvs.getContext('2d');
this._line;
this._circle;
this._gravity = 0.2;
this._bounce = -0.6;
this._vx = 0;
this._vy = 0;
// タイマー関連
this._animID;
this._isAnim = 0;
this._FPS = 60;
this._frame = 0;
this._startTime;
this._nowTime;
this._init();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Private and protected
//////////////////////////////////
_init() {
this._cvs.style.backgroundColor = "#eeeeee";
// 角度のついた反射面を描画
this._line = new Line(this._ctx, 0, 0, 250, 0);
this._line.x = 50;
this._line.y = 200;
// 角度をラジアンに変換して渡す
this._line.rotation = 10 * Math.PI / 180;
this._circle = new Circle(this._ctx, 100, 100, 30);
this._startTime = performance.now();
this._mainLoop();
}
_mainLoop() {
this._nowTime = performance.now();
let elapsedTime = this._nowTime - this._startTime;
let idealTime = this._frame * (1000 / this._FPS);
if (idealTime < elapsedTime) {
this._ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this._cvs.width, this._cvs.height);
// ①線の矩形領域をオブジェクト(x, y, 幅, 高さ)で取得
let bounds = this._line.getBounds();
// ボールに速度を設定.Y軸に重力値を適用
this._vy += this._gravity;
this._circle.x += this._vx;
this._circle.y += this._vy;
// ②ボールが線上にあるか判定
if (this._circle.x + this._circle.radius > bounds.x
&& this._circle.x - this._circle.radius < bounds.x + bounds.width) {
// 角度のサインとコサインを取得
let cos = Math.cos(this._line.rotation);
let sin = Math.sin(this._line.rotation);
// 線を基準にしたボールの位置の取得
let x1 = this._circle.x - this._line.x;
let y1 = this._circle.y - this._line.y;
// 座標の回転
let x2 = cos * x1 + sin * y1;
let y2 = cos * y1 - sin * x1;
// 速度の回転
let vx1 = cos * this._vx + sin * this._vy;
let vy1 = cos * this._vy - sin * this._vx;
// ボールが線に当たったか判定
if (y2 > 0 - this._circle.radius) {
// 回転させた値を使った跳ね返りの実行
y2 = -this._circle.radius;
vy1 *= this._bounce;
}
// 全てを回転させて元状態に戻す
x1 = cos * x2 - sin * y2;
y1 = cos * y2 + sin * x2;
this._vx = cos * vx1 - sin * vy1;
this._vy = cos * vy1 + sin * vx1;
this._circle.x = this._line.x + x1;
this._circle.y = this._line.y + y1;
}
this._circle.draw();
this._line.draw();
this._frame++;
if (elapsedTime >= 1000) {
this._startTime = this._nowTime;
this._frame = 0;
}
}
this._animID = requestAnimationFrame(this._mainLoop.bind(this));
}
}
複数の反射面を跳ね返らせる
最後に反射面を4つに増やしてみる。
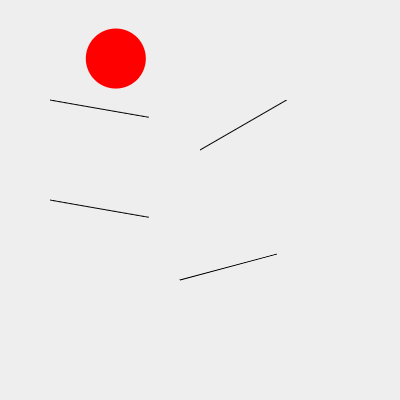
4つの反射面を跳ね返り落下していく処理を担当するAngleBounce3クラス。
import { Line } from "./line.js";
import { Circle } from "./circle.js";
/**
* 角度のついた跳ね返り運動3(anglebounce3.js)
*/
export class AngleBounce3 {
constructor() {
this._cvs = document.getElementById('canvas');
this._ctx = this._cvs.getContext('2d');
// ①反射面の線を4本分配列で用意
this._lines = [];
this._NUM_LINES = 4;
this._circle;
this._gravity = 0.2;
this._bounce = -0.6;
this._vx = 0;
this._vy = 0;
// タイマー関連
this._animID;
this._isAnim = 0;
this._FPS = 60;
this._frame = 0;
this._startTime;
this._nowTime;
this._init();
}
//////////////////////////////////
// Private and protected
//////////////////////////////////
_init() {
this._cvs.style.backgroundColor = "#eeeeee";
// ②角度のついた反射面を描画
let lx = [50, 200, 50, 180];
let ly = [100, 150, 200, 280];
let lr = [10, -30, 10, -15];
for (let i = 0; i < this._NUM_LINES; i++) {
this._lines[i] = new Line(this._ctx, 0, 0, 100, 0);
this._lines[i].x = lx[i];
this._lines[i].y = ly[i];
this._lines[i].rotation = lr[i] * Math.PI / 180;
}
this._circle = new Circle(this._ctx, 100, 0, 30);
this._startTime = performance.now();
this._mainLoop();
}
_checkLine(line) {
// 線の矩形領域をオブジェクト(x, y, 幅, 高さ)で取得
let bounds = line.getBounds();
// ボールが線上にあるか判定
if (this._circle.x + this._circle.radius > bounds.x
&& this._circle.x - this._circle.radius < bounds.x + bounds.width) {
// 角度のサインとコサインを取得
let cos = Math.cos(line.rotation);
let sin = Math.sin(line.rotation);
// 線を基準にしたボールの位置の取得
let x1 = this._circle.x - line.x;
let y1 = this._circle.y - line.y;
// 座標の回転
let x2 = cos * x1 + sin * y1;
let y2 = cos * y1 - sin * x1;
// 速度の回転
let vx1 = cos * this._vx + sin * this._vy;
let vy1 = cos * this._vy - sin * this._vx;
// ⑤ボールが線に当たったか判定
if (y2 > 0 - this._circle.radius && y2 < vy1) {
// 回転させた値を使った跳ね返りの実行
y2 = -this._circle.radius;
vy1 *= this._bounce;
}
// 全てを回転させて元状態に戻す
x1 = cos * x2 - sin * y2;
y1 = cos * y2 + sin * x2;
this._vx = cos * vx1 - sin * vy1;
this._vy = cos * vy1 + sin * vx1;
this._circle.x = line.x + x1;
this._circle.y = line.y + y1;
}
line.draw();
}
_mainLoop() {
this._nowTime = performance.now();
let elapsedTime = this._nowTime - this._startTime;
let idealTime = this._frame * (1000 / this._FPS);
if (idealTime < elapsedTime) {
this._ctx.clearRect(0, 0, this._cvs.width, this._cvs.height);
// ③ボールに速度を設定.Y軸に重力値を適用
this._vy += this._gravity;
this._circle.x += this._vx;
this._circle.y += this._vy;
// ④ボールと各線の跳ね返り処理を線の数だけ実行
for (let i = 0; i < this._NUM_LINES; i++) {
if (this._checkLine(this._lines[i])) {
break;
}
}
this._circle.draw();
this._frame++;
if (elapsedTime >= 1000) {
this._startTime = this._nowTime;
this._frame = 0;
}
}
this._animID = requestAnimationFrame(this._mainLoop.bind(this));
}
}
①反射面を4つにするため、配列で管理。
②4つの反射面をfor文で作成。
③ボールは今までと同じ1つのため、ボールに対する重力や速度の計算、適用はメインループで1度だけ行う。
④反射面となる線とボールの跳ね返り処理は、線が4つあるため独立した関数にまとめた。その_checkLine()をfor文で各線分呼び出す。
⑤if文の条件式の後半に「&& y2 < vy1」を追加している。これがないと跳ね返ったボールが上の線を超えると、超えた線に登ってしまう。
参考図書

コメント